Balancing Your Macronutrients: Tips for a Healthy Diet

Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for overall health and well-being. Macronutrients—proteins, carbohydrates, and fats—play essential roles in our bodies, and achieving the right balance among them is key to optimizing health. Understanding how to balance these macronutrients can help you meet your nutritional needs, support energy levels, and promote overall wellness. Here’s a guide to effectively balance your macronutrients for a healthier diet.
Understanding Macronutrients
Macronutrients are nutrients required in large amounts to provide energy and support various bodily functions. They are divided into three main categories:
- Proteins: Vital for tissue repair, muscle growth, and immune function. Proteins are made up of amino acids, some of which are essential, meaning they must be obtained through diet. Good sources include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.
- Carbohydrates: The body’s primary source of energy. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which fuels various bodily functions and physical activities. They can be found in foods like grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Carbohydrates are categorized into simple (sugars) and complex (starches and fiber) forms.
- Fats: Essential for hormone production, cell membrane integrity, and energy storage. Fats also help absorb fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, while trans fats and excessive saturated fats should be limited.
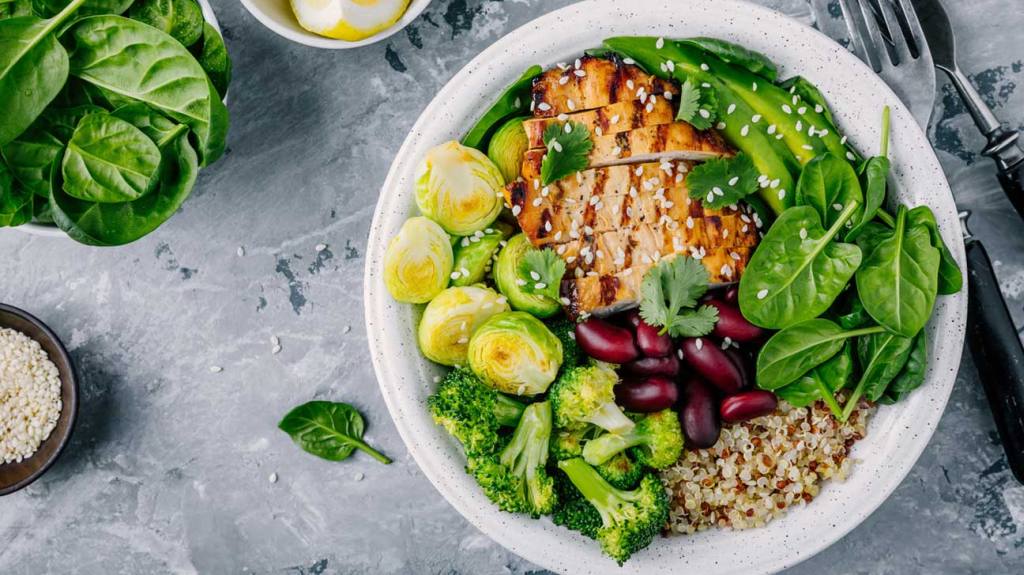

Determining Your Macronutrient Needs
Balancing your macronutrients starts with understanding how much of each you need. This can vary based on individual factors such as age, sex, activity level, and health goals. A general guideline is:
- Proteins: Aim for 10-35% of your total daily calories. For most adults, this translates to about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Active individuals or those aiming to build muscle may require more.
- Carbohydrates: Should comprise 45-65% of your daily caloric intake. Focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains and vegetables rather than refined sugars and starches.
- Fats: Make up about 20-35% of your total daily calories. Prioritize unsaturated fats and limit saturated fats to less than 10% of your daily intake. Avoid trans fats as much as possible.
Tips for Balancing Your Macronutrients
- Plan Your Meals Wisely
Balancing macronutrients involves planning meals that incorporate a variety of food sources. Include a source of protein, carbohydrate, and healthy fat in each meal. For example, a balanced lunch might consist of grilled chicken (protein), quinoa (carbohydrate), and a side of mixed greens with olive oil (fat).
- Choose Whole Foods
Whole, minimally processed foods are generally better sources of essential nutrients. Opt for lean meats, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. These foods provide a range of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, contributing to a more balanced diet.
- Monitor Portion Sizes
Portion control is key to achieving the right balance of macronutrients. Be mindful of serving sizes to avoid consuming excessive calories from any one macronutrient. Using smaller plates, measuring portions, and avoiding second helpings can help maintain balance.
- Adjust for Activity Levels
Your macronutrient needs may vary based on physical activity. If you’re highly active or engaging in strength training, you might need a higher protein intake to support muscle repair and growth. Conversely, less active individuals may need fewer carbohydrates to align with their energy expenditure.
Making Adjustments for Health Goals
Balancing macronutrients can be tailored to specific health goals, such as weight loss, muscle gain, or managing a health condition. For weight loss, a common approach is to reduce carbohydrate intake while maintaining adequate protein to preserve muscle mass. For muscle gain, increasing protein and overall caloric intake can support muscle growth.
Consulting with a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide personalized advice based on your individual health needs and goals. They can help you create a customized meal plan that aligns with your macronutrient requirements.
Conclusion
Balancing macronutrients is essential for achieving and maintaining a healthy diet. By understanding the roles of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, and how to proportion them appropriately, you can support your overall health and well-being. Incorporating a variety of whole foods, planning your meals thoughtfully, and adjusting your intake based on activity levels and health goals can help you achieve a balanced and nutritious diet.